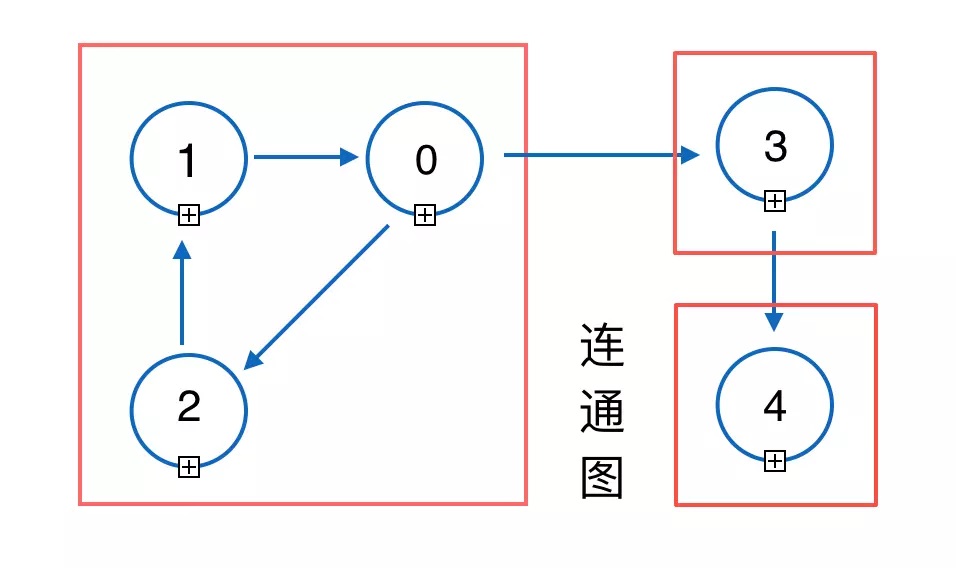
主要思路
这道题是一道比较裸的 Tarjan 题。我们用 Tarjan 算法来获得强连通分量,并且缩点成 DAG 森林,统计 DAG 上入度为 0 的个数即可。这里推荐一篇关于 Tarjan 算法的优秀讲稿:https://www.byvoid.com/zhs/blog/scc-tarjan
代码
// P2002.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int MX_N = 900200, MX_M = 902000;
int timeStamp[MX_N], low[MX_N], n, m, head[MX_N], current, idx, ans, belongs[MX_N], bcnt;
int deg[MX_N];
struct edge
{
int to, nxt;
} edges[MX_M << 1];
bool isInStack[MX_N], anses[MX_N];
stack<int> st;
vector<int> G[MX_N];
void addpath(int src, int dst)
{
edges[current].to = dst, edges[current].nxt = head[src];
head[src] = current++;
}
void dfs(int u)
{
timeStamp[u] = low[u] = ++idx;
isInStack[u] = true;
st.push(u);
for (int i = head[u]; i != -1; i = edges[i].nxt)
if (timeStamp[edges[i].to] == 0)
dfs(edges[i].to), low[u] = min(low[u], low[edges[i].to]);
else if (isInStack[edges[i].to])
low[u] = min(low[u], timeStamp[edges[i].to]);
if (timeStamp[u] == low[u])
{
bcnt++;
while (1)
{
int j = st.top();
st.pop();
isInStack[j] = false, belongs[j] = bcnt;
if (j == u)
break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int src, dst;
scanf("%d%d", &src, &dst);
addpath(src, dst);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (timeStamp[i] == 0)
dfs(i);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int e = head[i]; e != -1; e = edges[e].nxt)
if (belongs[i] != belongs[edges[e].to])
G[belongs[e]].push_back(belongs[edges[e].to]), deg[belongs[edges[e].to]]++;
for (int i = 1; i <= bcnt; i++)
if (deg[i] == 0)
ans++;
printf("%d", ans);
return 0;
}